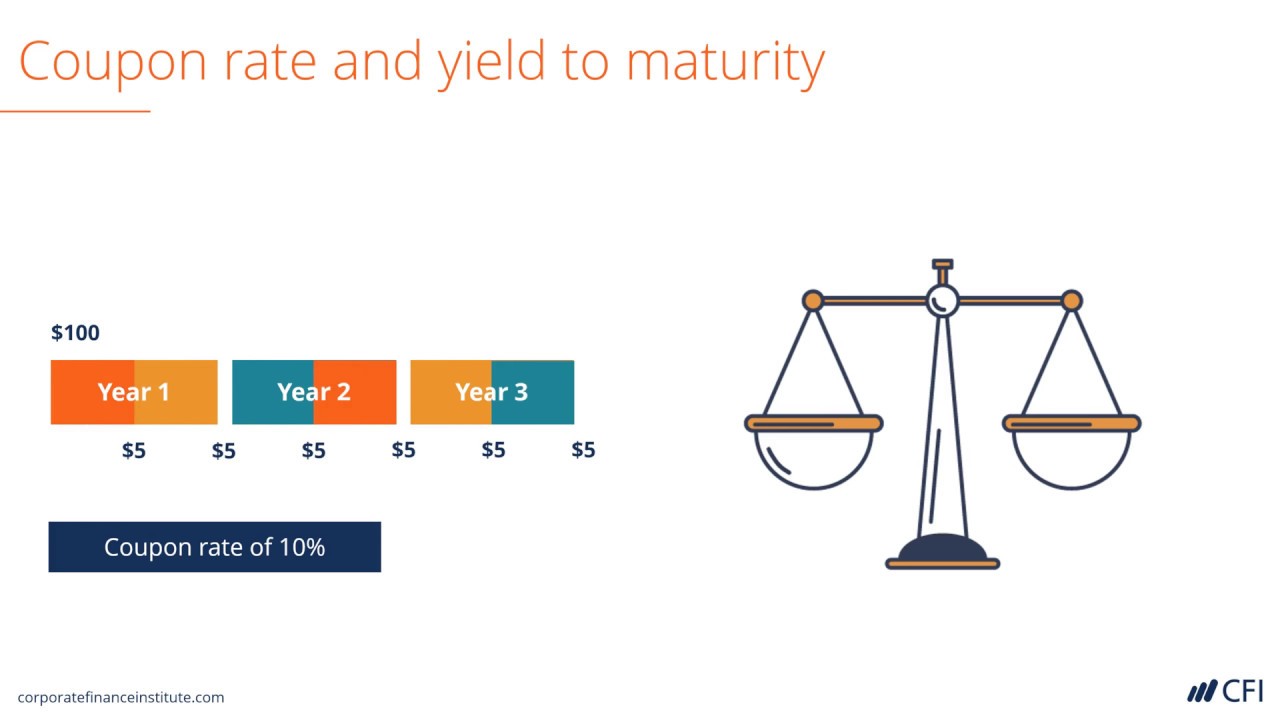
43 define zero coupon bond
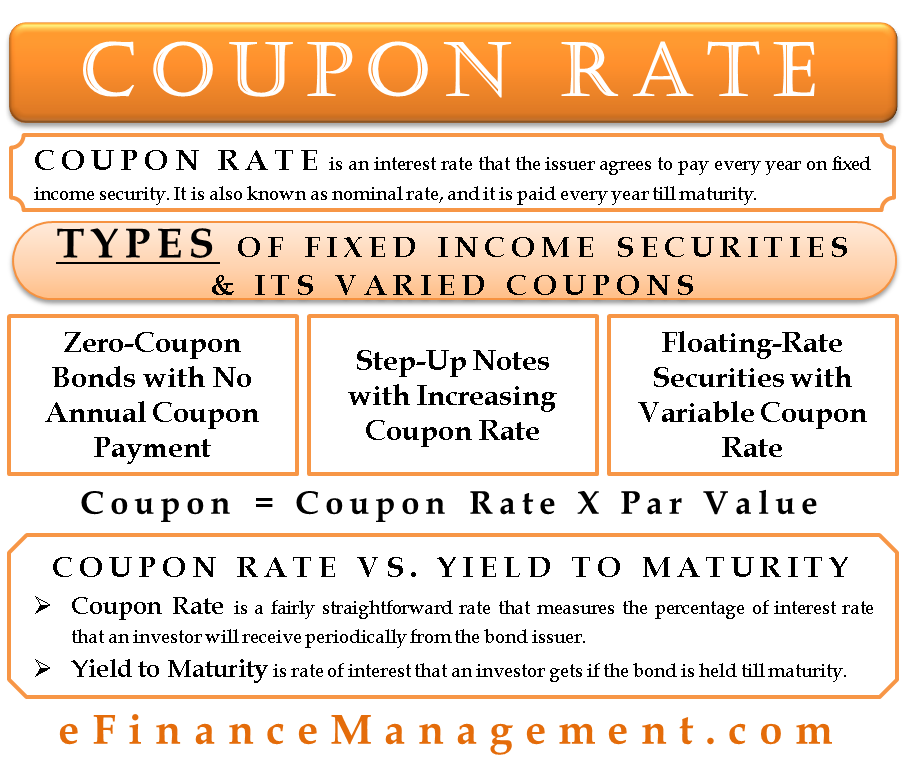
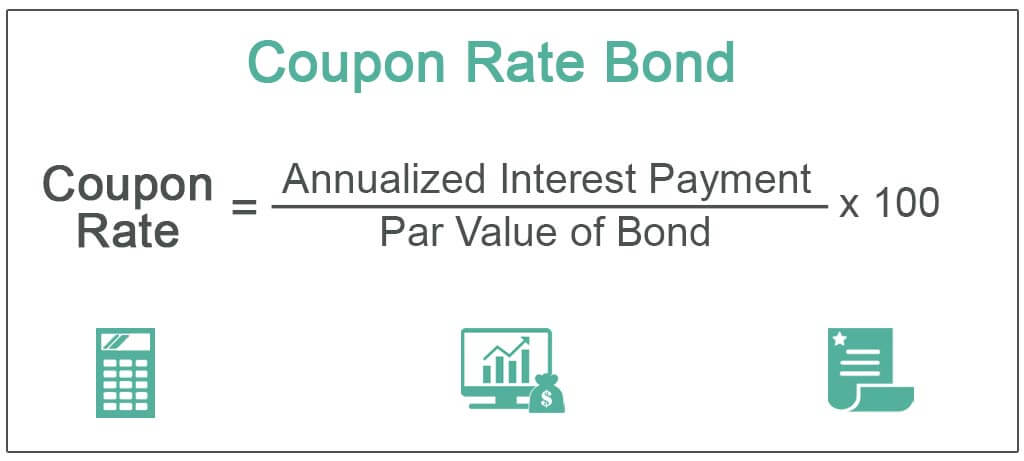
Bond Definition: What Are Bonds? – Forbes Advisor Aug 24, 2021 · Coupon: The fixed rate of interest that the bond issuer pays its bondholders. Using the $1,000 example, if a bond has a 3% coupon, the bond issuer promises to pay investors $30 per year until the ... Bootstrapping Zero Curve & Forward Rates 22/10/2016 · The discounted cash flows & zero rates for later tenors will be solved for using the par bond assumption and the zero rates derived for the earlier tenors. This is illustrated in the steps that follow. 5. Let us start with the shortest tenor bond, the 0.25 year bond. Its cash flows are coupon and principal payable at maturity of 101.0075. The ...
Convexity of a Bond | Formula | Duration | Calculation The number of coupon flows (cash flows) change the duration and hence the convexity of the bond. The duration of a zero bond is equal to its time to maturity, but as there still exists a convex relationship between its price and yield, zero-coupon bonds have the highest convexity and its prices most sensitive to changes in yield.

Define zero coupon bond
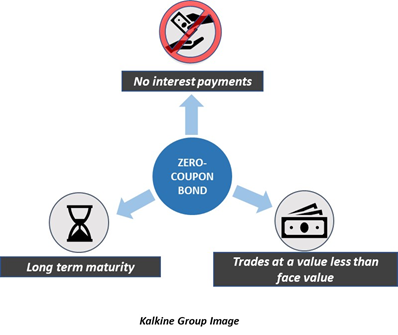
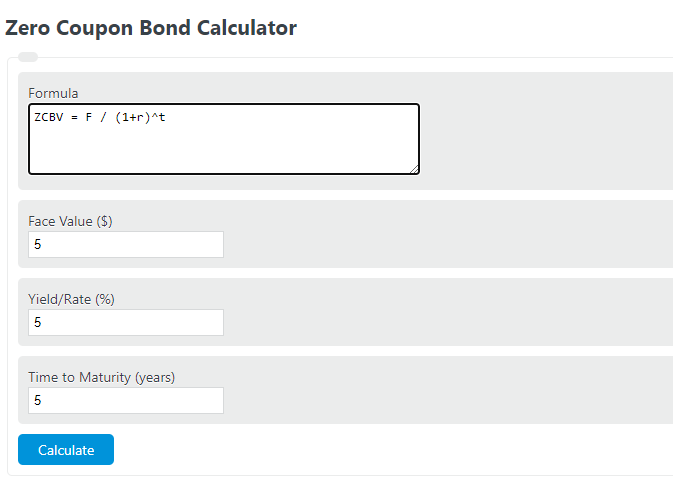
Convexity of a Bond | Formula | Duration | Calculation As a result, this bond has only one return: the payment of the nominal value at maturity. read more portfolio can be adjusted as to the that of a single zero-coupon bond by varying the nominal and maturity value of the zero-coupon bonds within the portfolio. However, the convexity of this portfolio is higher than the single zero-coupon bond ... Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Zero Coupon Bond Instead, investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due. The maturity dates on zero coupon bonds are usually long-term—many don’t mature for ten, fifteen, or more years. Bootstrapping Zero Curve & Forward Rates ... Oct 22, 2016 · The discounted cash flows & zero rates for later tenors will be solved for using the par bond assumption and the zero rates derived for the earlier tenors. This is illustrated in the steps that follow. 5. Let us start with the shortest tenor bond, the 0.25 year bond. Its cash flows are coupon and principal payable at maturity of 101.0075.
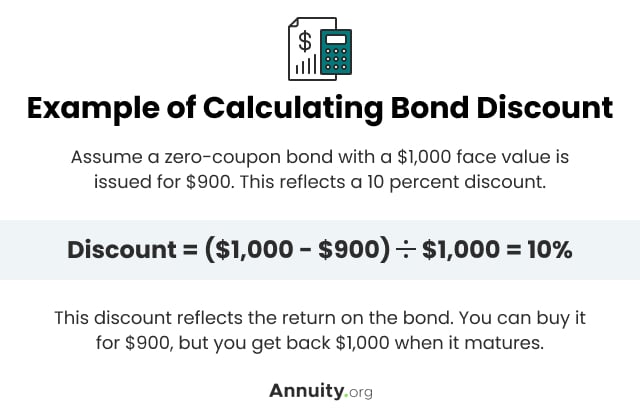
Define zero coupon bond. What Is Bond Yield? - Investopedia May 31, 2022 · Bond Yield: A bond yield is the amount of return an investor realizes on a bond. Several types of bond yields exist, including nominal yield which is the interest paid divided by the face value of ... Corporate Bonds | Investor.gov These are called zero-coupon bonds, because they make no coupon payments. Instead, the bond makes a single payment at maturity that is higher than the initial purchase price. For example, an investor may pay $800 to purchase a five-year, zero-coupon bond with a face value of $1,000. The company pays no interest on the bond for the next five years, and then, at … Answered: Define each of the following terms:c.… | bartleby A: A zero-coupon bond is also known as accrual bond because a zero coupon bond doesn't pay the coupon… Q: The discount bond sells for ____________ as maturity approaches. A: Bond is a debt instrument issued by companies and government. Answered: Define each of the following terms:c.… | bartleby A: A zero-coupon bond is also known as accrual bond because a zero coupon bond doesn't pay the coupon… Q: The discount bond sells for ____________ as maturity approaches. A: Bond is a debt instrument issued by companies and government.
Synonym Synonym's The Classroom covers more than just homework and study tips. It's your comprehensive resource for tips about classroom both inside and out. What Is Bond Yield? - Investopedia 31/05/2022 · Bond Yield: A bond yield is the amount of return an investor realizes on a bond. Several types of bond yields exist, including nominal yield which is the interest paid divided by the face value of ... Understanding Fixed-Income Risk and Return - CFA Institute Sources of return on a fixed-rate bond investment include the receipt and reinvestment of coupon payments and either the redemption of principal if the bond is held to maturity or capital gains (or losses) if the bond is sold earlier. Fixed-income investors holding the same bond may have different interest rate risk exposures if their investment horizons differ. Yield spread - Wikipedia There are several measures of yield spread relative to a benchmark yield curve, including interpolated spread , zero-volatility spread , and option-adjusted spread (OAS). It is also possible to define a yield spread between two different maturities of otherwise comparable bonds. For example, if a certain bond with a 10-year maturity yields 8% ...
Bond Definition: What Are Bonds? – Forbes Advisor 24/08/2021 · Coupon: The fixed rate of interest that the bond issuer pays its bondholders. Using the $1,000 example, if a bond has a 3% coupon, the bond issuer promises to pay investors $30 per year until the ... Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Zero coupon bonds are bonds that do not pay interest during the life of the bonds. Instead, investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due. Skip to main content An official website of the United States government. Here’s how you know. Here’s how you know. The … Understanding Fixed-Income Risk and Return - CFA Institute The total return is the future value of reinvested coupon interest payments and the sale price (or redemption of principal if the bond is held to maturity).The horizon yield (or holding period rate of return) is the internal rate of return between the total return and purchase price of the bond. Coupon reinvestment risk increases with a higher ... Bootstrapping Zero Curve & Forward Rates ... Oct 22, 2016 · The discounted cash flows & zero rates for later tenors will be solved for using the par bond assumption and the zero rates derived for the earlier tenors. This is illustrated in the steps that follow. 5. Let us start with the shortest tenor bond, the 0.25 year bond. Its cash flows are coupon and principal payable at maturity of 101.0075.
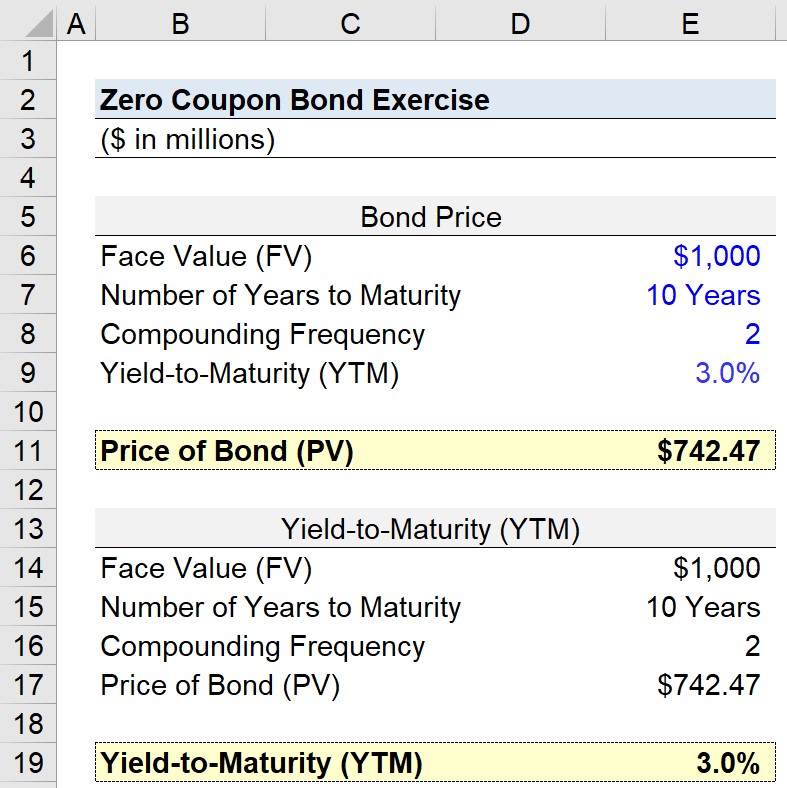
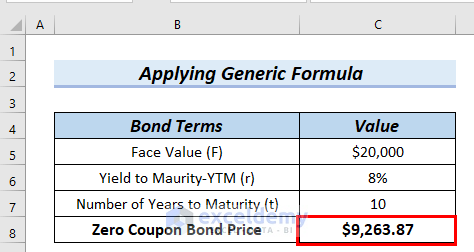
Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Zero Coupon Bond Instead, investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due. The maturity dates on zero coupon bonds are usually long-term—many don’t mature for ten, fifteen, or more years.
Convexity of a Bond | Formula | Duration | Calculation As a result, this bond has only one return: the payment of the nominal value at maturity. read more portfolio can be adjusted as to the that of a single zero-coupon bond by varying the nominal and maturity value of the zero-coupon bonds within the portfolio. However, the convexity of this portfolio is higher than the single zero-coupon bond ...















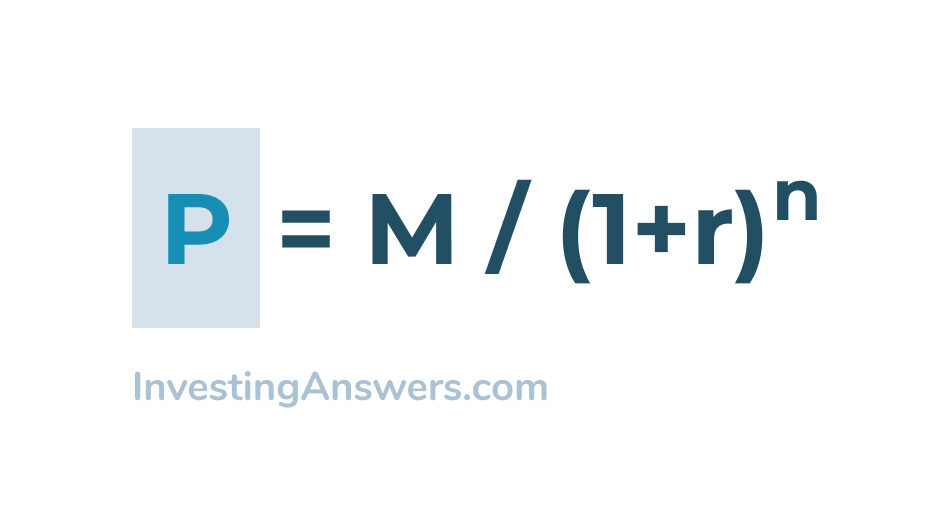




/dotdash_Final_Bond_Apr_2020-01-8b83e6be5db3474e896a93c1c1a9f169.jpg)






Post a Comment for "43 define zero coupon bond"